Nuts
Brazil nut
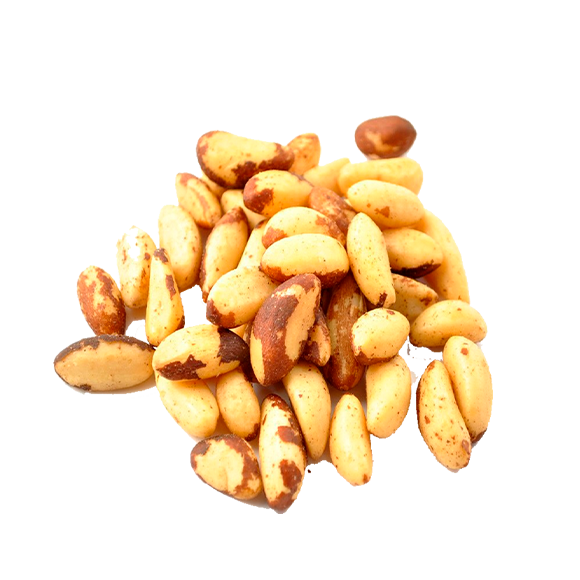


Brazil nut, which has a high protein and caloric value. The seed provides selenium mineral, which is important for fighting the free radicals present in the body. Brazil nut is also rich in fiber, calcium, and iron. Even though they have a high calorie content, these nuts are efficient for those seeking to lose weight, because they are rich in monounsaturated fats that stimulate the metabolism and the burning of fat.
The seeds can be eaten raw or roasted, and are also used in the production of flour, sweets, and ice cream. The oil extracted from the Brazil nut can also be used in the cosmetics industry and in the manufacture of paints.
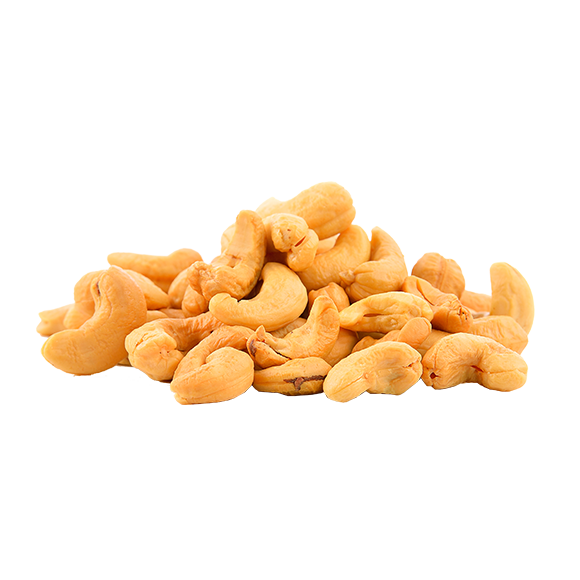
The cashew tree is typical of Northeastern Brazil, producing the cashew, which in botanical terms is not considered a fruit. The actual fruit of the cashew tree is the cashew nut.
This is because scientifically a fruit is a structure created from the ovary of the flower to protect its seeds.
In this case, it is the nut that is born from the ovary of the flower. The part of the plant that develops the yellowish pulp, which we know as the cashew itself, is called the peduncle. Therefore, it is classified as a pseudo-fruit or an accessory fruit.
The consumption of cashew nuts causes glucose and cholesterol to be absorbed more slowly during the meal, avoiding the peaks of both, which are harmful for those with diabetes and high cholesterol, respectively. The fibers are responsible for this effect.
Cashew nuts help fight the free radicals that degrade collagen, proteins that act to support the skin. When this degradation occurs, wrinkles and sagging of the skin are caused.
DETAILS ABOUT PRODUCTION CAPACITY, SEASONALITY, AND OTHER CHARACTERISTICS:
Our production capacity is 32,000 kg/month.